Uncover the truth behind corporate sustainability with 7 powerful reporting methods. From ESG to TBL, carbon to integrated, dive into the types of sustainability reporting and discover how companies are driving change.
Table of Contents
Types of Sustainability Reporting
There are seven types of sustainability reporting, including ESG reporting, Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR) reporting, Global Reporting Initiative (GRI) reporting, Carbon reporting, Triple Bottom Line (TBL) reporting, Integrated reporting, and Sustainability accounting.
1. Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) Reporting
Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) reporting is a crucial tool for companies to communicate their sustainability performance and impact to stakeholders.
This type of reporting provides a comprehensive view of a company’s environmental, social, and governance practices and their effect on the world around us.
The ESG reporting framework focuses on three key areas: the environment, social issues, and governance.
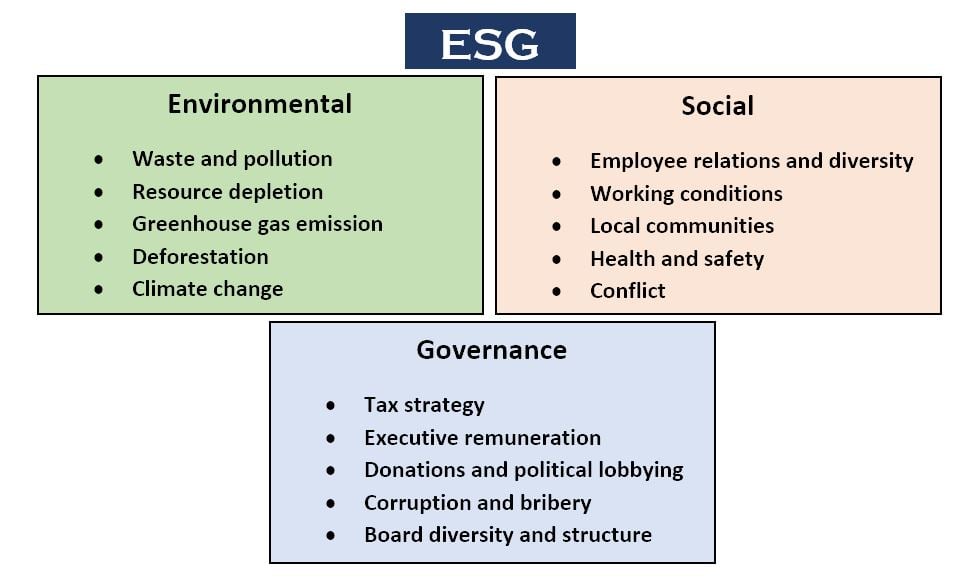
In the environmental aspect, ESG reporting looks at a company’s carbon footprint, waste management practices, and efforts to reduce its impact on the environment.
The social aspect examines a company’s practices related to human rights, labor standards, and community engagement. The governance aspect focuses on a company’s corporate governance practices, such as executive compensation, board structure, and ethical behavior.
ESG reporting is becoming increasingly important as consumers, investors, and governments demand more transparency and accountability from companies. This type of reporting helps companies to demonstrate their commitment to sustainability and the positive impact they are having on the world.
It also provides stakeholders with valuable information about a company’s sustainability practices, allowing them to make informed decisions about their investments, purchases, and support for the company.
In addition to benefiting stakeholders, ESG reporting also provides benefits to the companies themselves. By tracking and reporting on their sustainability practices, companies can identify areas for improvement, set achievable sustainability goals, and measure their progress toward these goals.
This can lead to cost savings, improved reputation, and increased competitiveness in the market.
2. Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR) Reporting

Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR) reporting is a crucial tool for companies to communicate their commitment to social and environmental responsibility. This type of reporting focuses on a company’s social and environmental practices and their impact on the world.
CSR reporting helps companies to demonstrate their commitment to sustainability and the positive impact they are having on society.
By tracking and reporting on their social and environmental practices, companies can identify areas for improvement, set achievable sustainability goals, and measure their progress toward these goals. This can lead to an improved reputation, increased competitiveness, and cost savings.
For stakeholders, CSR reporting provides valuable information about a company’s social and environmental practices, allowing them to make informed decisions about their investments, purchases, and support for the company.
By supporting sustainable companies, stakeholders can drive positive change in the world.
3. Global Reporting Initiative (GRI) Reporting
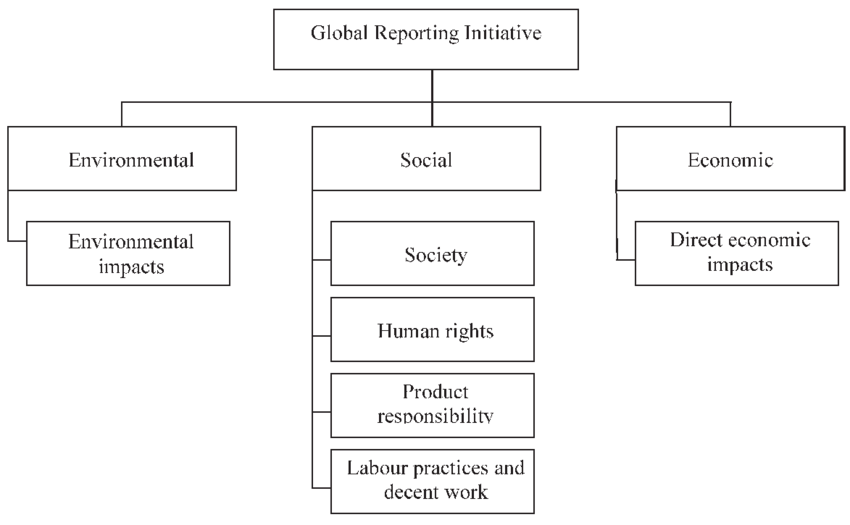
The Global Reporting Initiative (GRI) is a widely recognized framework for sustainability reporting that provides guidelines for companies to report on a range of sustainability issues.
This includes environmental, social, and governance performance, providing a comprehensive view of a company’s sustainability practices and their impact on the world.
The GRI framework is designed to be flexible and responsive to the changing needs of companies and stakeholders.
It provides a set of guidelines and indicators that companies can use to report on their sustainability practices, and it also provides a common language for stakeholders to understand and compare sustainability reports.
One of the key benefits of GRI reporting is its ability to provide a consistent and comparable view of a company’s sustainability practices.
This allows stakeholders to easily compare the sustainability performance of different companies, making it easier to identify the leaders and laggards in the sustainability arena.
For companies, using the GRI framework can help to improve their sustainability performance by providing a structured approach to reporting on their practices and impact. It can also help companies to identify areas for improvement and set achievable sustainability goals.
4. Carbon Reporting

Carbon reporting is a specialized form of sustainability reporting that focuses specifically on a company’s carbon footprint. This includes measuring and reporting on the company’s greenhouse gas emissions and its efforts to reduce them.
The importance of carbon reporting has increased in recent years as the world has become more aware of the negative impact of greenhouse gas emissions on the environment.
Companies are under increasing pressure from stakeholders, including consumers, investors, and governments, to reduce their carbon footprint and take action to address climate change.
Carbon reporting provides a structured approach for companies to track and report on their emissions, allowing them to measure their progress toward reducing their carbon footprint.
It also provides valuable information for stakeholders, including investors, about a company’s efforts to address climate change and the impact of these efforts on the company’s bottom line.
In addition to providing benefits for stakeholders and the environment, carbon reporting can also provide benefits for companies.
By tracking and reporting on their emissions, companies can identify areas for improvement, set achievable sustainability goals, and measure their progress toward these goals.
This can lead to cost savings, improved reputation, and increased competitiveness in the market.
5. Triple Bottom Line (TBL) Reporting

Triple Bottom Line (TBL) reporting is a comprehensive approach to sustainability reporting that focuses on the three pillars of sustainability: economic, social, and environmental performance. This type of reporting provides a holistic view of a company’s sustainability practices and their impact on the world.
TBL reporting recognizes that sustainability is not just about the environment but also about the economic and social impact of a company’s practices. It provides a balanced view of a company’s performance, including its financial performance, social impact, and environmental impact.
TBL reporting is becoming increasingly important as consumers, investors, and governments demand more transparency and accountability from companies. This type of reporting helps companies to demonstrate their commitment to sustainability and the positive impact they are having on the world.
It also provides stakeholders with valuable information about a company’s sustainability practices, allowing them to make informed decisions about their investments, purchases, and support for the company.
In addition to benefiting stakeholders, TBL reporting also provides benefits to the companies themselves. By tracking and reporting on their sustainability practices, companies can identify areas for improvement, set achievable sustainability goals, and measure their progress toward these goals.
This can lead to cost savings, improved reputation, and increased competitiveness in the market.
6. Integrated Reporting
Integrated reporting is a comprehensive approach to reporting that provides a holistic view of a company’s performance.
This type of reporting combines financial and non-financial information, including sustainability metrics, to give stakeholders a complete picture of a company’s performance and impact on the world.
Integrated reporting recognizes that a company’s success is not just about its financial performance but also about its social and environmental impact. It provides a comprehensive view of a company’s sustainability practices, including its financial performance, social impact, and environmental impact.
The benefits of integrated reporting are significant for both companies and stakeholders. For companies, integrated reporting provides a structured approach to reporting on their sustainability practices and impact, allowing them to identify areas for improvement, set achievable sustainability goals, and measure their progress toward these goals.
This can lead to cost savings, improved reputation, and increased competitiveness in the market.
For stakeholders, integrated reporting provides valuable information about a company’s sustainability practices and impact, allowing them to make informed decisions about their investments, purchases, and support for the company. Integrated reporting also helps to increase transparency and accountability, making it easier for stakeholders to understand a company’s sustainability practices and impact.
7. Sustainability Accounting
Sustainability accounting is a specialized form of accounting that focuses on the financial and economic aspects of sustainability.
This type of accounting provides information about the costs and benefits of sustainability initiatives, allowing companies to understand the financial impact of their sustainability practices.
Sustainability accounting is becoming increasingly important as companies look for ways to improve their sustainability performance and demonstrate their commitment to sustainability to stakeholders.
This type of accounting helps companies to understand the financial impact of their sustainability initiatives, including the costs of sustainability measures and the benefits they provide.
For stakeholders, sustainability accounting provides valuable information about a company’s financial commitment to sustainability and the impact of these initiatives on the company’s bottom line.
This allows stakeholders to make informed decisions about their investments, purchases, and support for the company.
In addition to benefiting stakeholders, sustainability accounting also provides benefits to the companies themselves. By tracking and reporting on the costs and benefits of their sustainability initiatives, companies can identify areas for improvement, set achievable sustainability goals, and measure their progress toward these goals.
This can lead to cost savings, improved reputation, and increased competitiveness in the market.
Conclusion
Sustainability reporting is a critical tool for companies to communicate their commitment to sustainability and the positive impact they are having on the world.
Each type of reporting provides a different perspective on a company’s sustainability performance and impact, and companies may choose to use a combination of these types of reporting to provide a comprehensive picture of their sustainability efforts.
Sustainability reporting provides valuable information for stakeholders, including investors, consumers, and governments, allowing them to make informed decisions about their investments, purchases, and support for sustainable companies.
It also provides companies with a structured approach to tracking and reporting on their sustainability practices and impact, allowing them to identify areas for improvement, set achievable sustainability goals, and measure their progress toward these goals.
In the end, sustainability reporting plays a crucial role in driving positive change and supporting sustainable practices worldwide.
Companies that prioritize sustainability reporting and take action to improve their sustainability performance will not only benefit the environment and society but also position themselves as leaders in the market and reap the benefits of increased reputation and competitiveness.
References
- Curbing Climate Change: The Paris Agreement and the Power of CCUS. https://www.linkedin.com/pulse/curbing-climate-change-paris-agreement-power-ccus-aman-goswami
- How Big Tech Supports Strategic Growth. https://resources.kahua.com/blog/how-big-tech-supports-strategic-growth
- Does Triple Bottom Line reporting improve hotel performance?. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S027843191100140X
- Sustainalytics” (Website) – https://www.sustainalytics.com/
- Global Reporting Initiative” (Website) – https://www.globalreporting.org/
- ESG investing: everything you need to know about it | Sleek. https://sleek.com/au/resources/esg-investing/

